1) Goat farming
The Ultimate Guide to Goat
FarmingGoat farming is an increasingly popular venture for both small-scale and commercial farmers. With their hardy nature, adaptability, and numerous products, goats can be a rewarding investment. Whether you’re considering raising goats for milk, meat, fiber, or as pets, this guide will provide essential insights to help you get started.
Why Choose Goat Farming?
1. Diverse Products
Milk Goat milk is rich in nutrients and often easier to digest than cow’s milk.
Meat Goat meat, known as chevon, is lean and gaining popularity in various cuisines.
Fiber Breeds like Angora and Cashmere provide high-quality fibers.
Land Management Goats are excellent for clearing brush and controlling weeds.
2.Low Maintenance Goats require less space than larger livestock and can thrive in various environments.
3.Friendly and Social Animals Goats are known for their curious and playful nature, making them enjoyable to raise.
Goat Farming
Importance of rearing sheep and goats In our country considering the domestic animals, the employment characteristic of goats and sheep is widely available for the weaker sections.
Goat sheep skin is widely used in leather industries. Wool from sheep and hair wool from the pulp is used in the weaving industry.
Manure from goats and sheep is superior to that of cows and buffaloes and contains twice as much potassium as conventional manures.Breeds of goats.
Indigenous caste
1) Osmanabadi

2) Sangamneri

3) Jamnapari
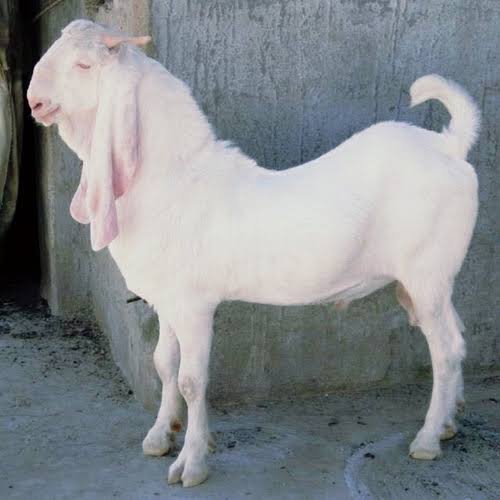

4) Shirohi

#Foreign caste
1) Sanen

2) African Boar

3) Alpine

4) Angora

5) Toggenberg Breeds of sheep.

Indigenous breeds of sheep.
1) Deccani

2) Nellore

3) Bannur

4) Madgyal.

Breeding of goats. Breeding period of goats.
Puberty period-
1) Average 7 to 10 months.
2) Age at first conception.
2) Feeding
1)Dicot
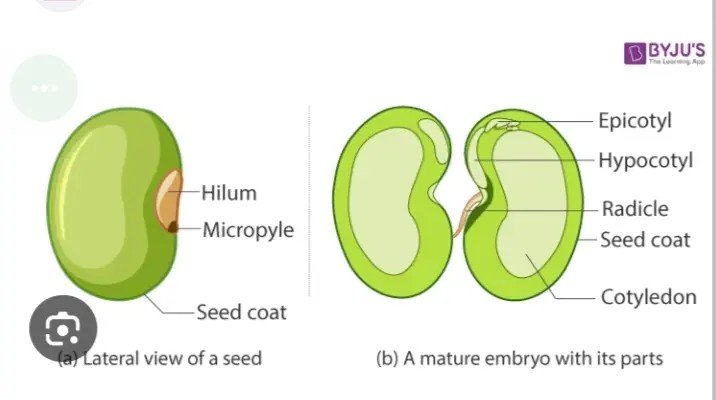
Dicot stems have a ring of vascular bundles, composed of xylem and phloem, that divide the ground tissue into the outer cortex and central pith. Dicot vascular bundles have an additional component, not present in monocot stems, called cambium.
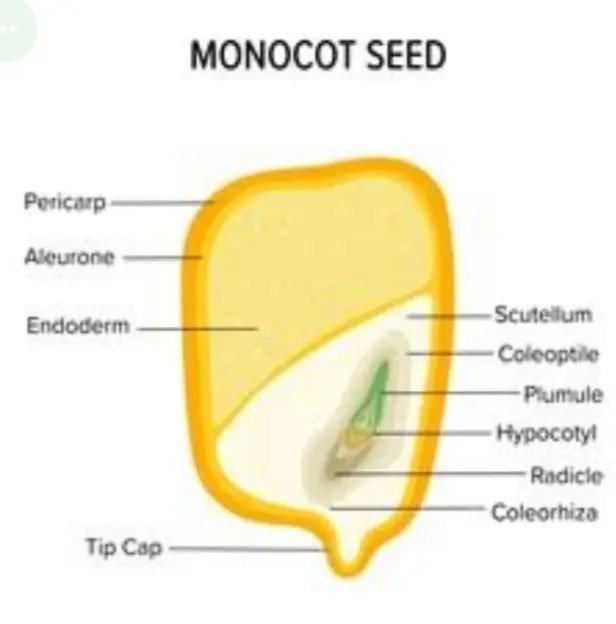
2)Monocot
Monocot seeds are seeds that are made out of a single (mono) embryonic leaf or cotyledon. Dicot seeds are seeds made up of two embryonic leaves or cotyledons. Monocot seeds have thin and tiny cotyledons. Dicot seeds have fleshy cotyledons that store food resources.
3)Dry fodder
Fodder is a type of food made from farming or other agricultural processes for feeding domesticated animals like cattle, cow, bull, buffalo, rabbit, horses etc. Fodder can only be consumed or eaten by animals. It is not for human beings. Examples for fodder are. grass, dried hay, straw etc.

4)Concentrated feed
Concentrates: Concentrates refer to animal feeds that are rich in energy and/or protein but low in fiber, such as corn, soybean meal, oats, wheat, molasses, etc. Crude Fat: Crude fat is an estimate of the total fat content of feeds taken from older collection of methods known as proximate methodology.
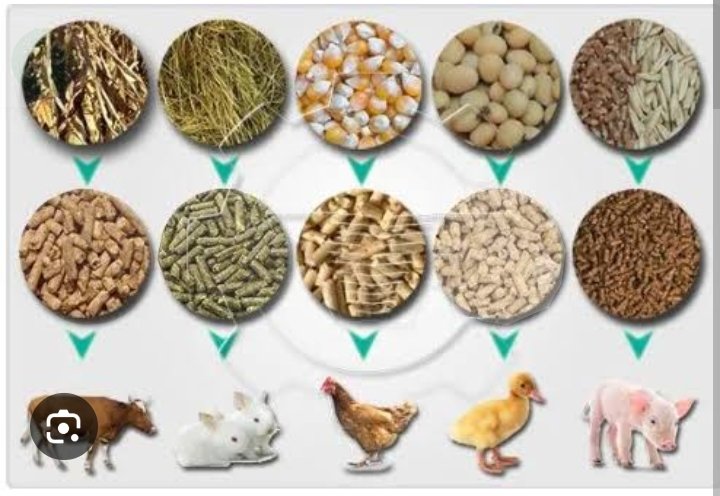

According to weight food has been given to animal.

3) Soil testing
Sampling of soil.
Taking a good representative soil sample is an important step in the soil analysis process. It is necessary to take the sample in a scientific manner in order to get accurate analytical results.
The soil sample taken should be representative of the area of land sampled. According to the type of soil, the land should be divided for sampling. Several samples taken from the same section should be combined and divided into four parts by mixing well.
Remove the two facing parts and rejoin the remaining two parts. After such division, usually half a kg of soil should be stored in a plastic or cloth bag and the bag should be properly labeled.
Colour Comparator color Comparator has been used in the testing method of pH, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Organic Carb.This colorimeter has two parts.1. Color Chart2. Color ComparatorUnitDifferent four colors of the above given four components are given in the Color Chart set.The color chart of the component to be tested should be kept in the color measuring unit (Comparator Unit). The color chart can easily be placed in the colorimeter or removed from the colorimeter.
Also, another element can be tested by changing the color chart.How to use a colorimeterPlace the color chart of the component to be tested in the colorimeter unit. The colorimeter is now ready to test that element. To test the second component, remove the color chart of the first component from the colorimeter unit and place the color chart of the second component there.Note on pH Colorimetry.The colorimetric method consists of a colorimeter.The pH Color Comparator has ten color bands for pH 4.5 (highly acidic) to 9.0 (highly low), according to the pH value of the soil.
Note on Phosphorus and Nitrogen Colorimetry.Phosphorus and sodium testing methods include colorimeter. The colorimeter has five color compartments (pink/blue), the intensity of the color in the compartments depends on the amount of available nitrogen and phosphorus in the soil (kg per hectare).
Organic CurbColorimeter The organic carb test method consists of a colorimeter with six color compartments based on the amount (%) of organic carb in the soil.Color matching on the colorimeter Place the glass test tube in the colorimeter during color matching. Hold the colorimeter up to the light while matching the color of the water to the color on the colorimeter.(Make a color match by holding a colorimeter between the sunlight and the observer.)
Observe the amount of available nitrogen/phosphorus (kg per ha), organic matter (%) in the soil on the color.Field preparationLand Field preparation Fertilizer 50″ Nitrogen Full dese phosphorus full dese potassium so” Nitrogen plantation day after planting 30 N:P:K Kg / hector 1 Soil testing
Required Fertilizer dose
N = 140
P= 13
K = very high dose
Soil we test in lab
Example of we want to farming of potato crop
The Fertilizer needed in the framing.
Potato 120: 240:120
P= 240 x 25%
=300 Kg
N=120×50%
= 180kg
K=120-50%
= 60kg
4) Collecting leaves from diseased trees
Collecting leaves from diseased trees can be a crucial step in:
1. Disease diagnosis: Leaf samples help identify pathogens or pests.
2. Monitoring disease spread: Tracking infected areas and tree health.
3. Research and development: Studying diseased leaves aids in understanding disease mechanisms.
Precautions:
1. Wear protective gear (gloves, mask, eyewear).
2. Avoid touching healthy plants to prevent cross-contamination.
3. Store collected leaves in sealed bags or containers.
4. Follow local regulations for handling and disposing of diseased plant material.
Disease identification methods:
1. Visual inspection (symptoms, discoloration).
2. Microscopic examination (fungal spores, bacteria).
3. Molecular techniques (PCR, DNA sequencing)
4. Serological tests (antibody-based).
Common tree diseases:
1. Dutch elm disease
2. Oak wilt
3. Leaf spot diseases (e.g., anthracnose)

4. Powdery mildew
5. Root rot diseases
*Best practices for collecting leaves:
1Choose representative samples (affected and healthy areas)
2. Collect leaves from multiple trees (if possible).
3. Record tree species, location, and symptoms.
4. Handle leaves gently to prevent damage.
5. Store samples in a cool, dry place.Would you like information on specific tree
5) Collecting samples of infested leaves
Collecting samples of infested leaves is crucial for
1. Accurate pest identification
2. Disease diagnosis
3. Monitoring infestation levels
4. Research and development
Precautions:
1. Wear protective gear (gloves, mask, eyewear)
2. Avoid touching healthy plants to prevent cross-contamination
3. Store collected leaves in sealed containers or bags
4. Follow local regulations for handling and disposing of infested plant material
Sampling Methods
1. Random sampling: Collect leaves from multiple areas of the tree
2. Stratified sampling: Sample leaves from different sections (e.g., upper, middle, lower)
3. Systematic sampling: Collect leaves at regular intervals (e.g., every 10th leaf)
Tools Needed:
1. Pruning shears or scissors
2. Gloves
3. Collection containers or bags
4. Labels and markers
5. Camera (for documentation)
Sampling Considerations:
1. Choose freshly infested leaves
2. Collect leaves with varying levels of infestation
3. Include leaves with visible symptoms (e.g., holes, discoloration)
4. Record environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity)
5. Note tree species, age, and health
Common Leaf Infestations
1. Aphids
2. Whiteflies
3. Spider mites
4. Caterpillars (e.g., bagworms, leafrollers)
5. Fungal diseases (e.g., powdery mildew, leaf spot)
Laboratory Analysis
1. Microscopic examination
2. DNA sequencing
3. PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
4. Serological tests
5. Bioassays
Submission Guidelines
1. Contact local extension offices or diagnostic labs
2. Provide detailed information (tree species, symptoms, location)
3. Follow lab-specific submission Protocols would you like information on specific pest identification or sampling protocols?
5) Estimating animal weight
Estimating animal weight is crucial for various purposes, such as
1. Veterinary care
2. Livestock management
3. Meat production
4. Research_Methods for Estimating Animal Weight:
Visual Estimation
1. Body condition scoring (BCS)
2. Muscle mass evaluation
3. Fat coverage assessment
Measurements:
1. Weight tapes (e.g., cattle, horses)
2. Circumference measurements (e.g., chest, girth)
3. Length measurements (e.g., body length, height)
Formulas and Calculations
1. Weight estimation equations (e.g., based on body measurements)
2. Regression analysis
3. Allometric scaling
Technological Tools
1. Electronic scales
2. Weighing platforms
3. 3D imaging and scanning
. Ultrasound measurement
*Species-Specific Estimation Methods:
1. Cattle: Weight tapes, body condition scoring, and measurements (e.g., hip height, body length)
2. Swine: Weight tapes, body length, and circumference measurements
3. Sheep and Goats: Weight tapes, body condition scoring, and measurements (e.g., body length, girth)
4. Horses: Weight tapes, body condition scoring, and measurements (e.g., height, girth)
Accuracy and Limitations
1. Visual estimation: ±10-20% accuracy
2. Measurement-based methods: ±5-15% accuracy
3. Technological tools: ±1-5% accuracy
Factors Affecting Weight Estimation
1. Breed and genetics
2. Age and growth stage
3. Nutrition and feeding practices
4. Health status
5. Body Condition would you like information on estimating weight for a specific animal species or method?
6) Drawing of a drip irrigation system
Here’s a simple drawing of a drip irrigation system:
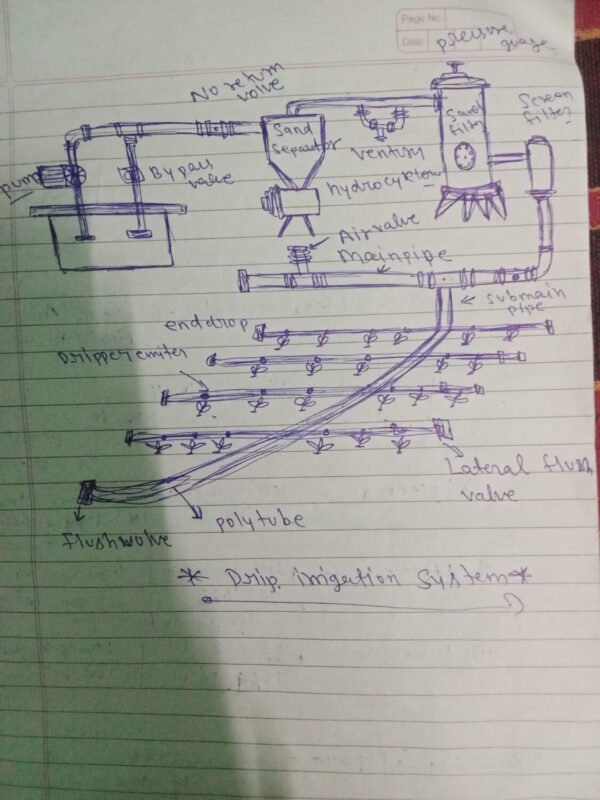
Components:
- Water Source (Pump/Tank)
- Filter (to prevent clogging)
- Pressure Regulator (to maintain pressure)
- Mainline (distribution pipe)
- Submain (smaller distribution pipe)
- Drip Tubing (with emitters)
- Emitters (drip points)
- End Cap (to seal the end of the drip tubing)
Drip Irrigation System Diagram:
+---------------+
| Water Source |
+---------------+
|
|
v
+---------------+
| Filter |
+---------------+
|
|
v
+---------------+
| Pressure Reg. |
+---------------+
|
|
v
+---------------+
| Mainline |
+---------------+
|
|
v
+---------------+
| Sub main |
+---------------+
|
|
v
+---------------+
| Drip Tubing |
|(with Emitters)|
+---------------+
|
|
v
+---------------+
| Emitters |
| (Drip Points)|
+---------------+
|
|
v
+---------------+
| End Cap |
+---------------+ Types of Drip Irrigation Systems:
- Surface Drip Irrigation
- Subsurface Drip Irrigation
- Micro-Irrigation
- Precision Irrigation
Would you like more information on drip irrigation.
7) Grafting process
Grafting is a horticultural technique used to join a piece of a stem (called a scion) from one plant onto the root system of another plant (called a rootstock).
This process allows farmers and gardeners to combine the desirable traits of different plants, such as fruit quality, disease resistance, and climate tolerance._Types of Grafting:
1.Budding -A single bud is taken from the scion and grafted onto the rootstock.
2. Whip and Tongue- A long, thin piece of the scion is grafted onto the rootstock using a whip-like motion.
3. Cleft Grafting- A piece of the scion is inserted into a cleft in the rootstock.
4. Splice Grafting- A piece of the scion is grafted onto the rootstock using a splice or overlap technique.
5. Inter stock Grafting- A piece of stem (called an inter stock) is grafted between the scion and rootstock.
_Grafting Process:
1. Prepare the Scion Select healthy, disease-free stems with desirable traits.
2. Prepare the Rootstock- Select healthy, disease-free rootstocks with desirable traits.
3. Make the Incision- Make a clean, angled incision on the scion and rootstock.
4. Join the Scion and Rootstock- Carefully place the scion onto the rootstock, ensuring the incisions align.
5. Secure the Graft- Use tape, twine, or wax to hold the scion in place.
8) Seed treatment
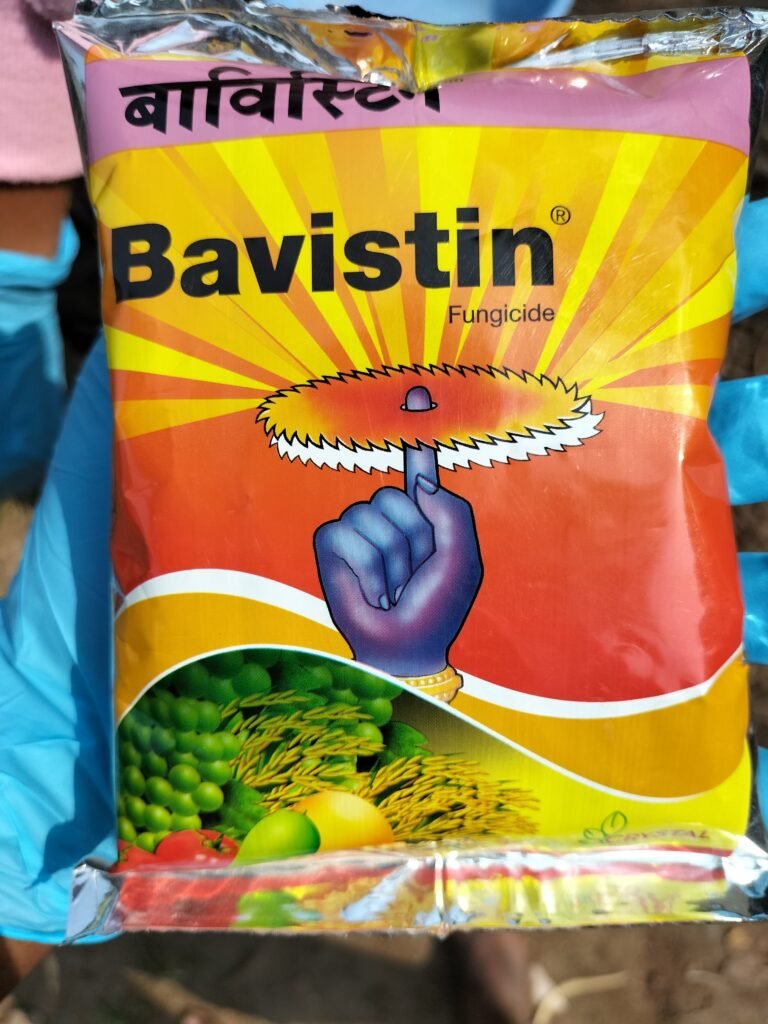

- Definition. Seeds are treated before sowing because seeds are treated with chemical biological physical and chemical (pgr) and bacterial growth agents to protect the crops from seed disease and to prevent them from spreading. . benefits . 1. Good seed germination.
- Increases plant immunity. .
- The pick comes in vigorous.
- Fixation of nitrogen in soil.
- And crops are protected from harmful bacteria in the soil. .
- Increase in yield of crops. .

- Reduces seedling mortality.
- Increases germination capacity of seeds.
- Materials for seed processing .
- Seed Fungicides Ozotobacter, Rhizobium, Sulphur(Smell) Water etc. . tools . Bag, bucket, waste paper, hand socks, marks etc.

9) Grass grows
Along with our yield in the field we also get grass which is not useful to us Characteristics of grass:-
They come early compared to our crops
Grows and spreads more in less water.
Grows tall early which prevents sunlight from reaching your crops. Damage caused:-
Cutting grass takes a lot of time and labor and costs a lot of money.

Crops suffer from lack of fertilizer.
Crops are not growing well. Types of grasses:-
Sursuri
Pambodya
Carrot grass
Chech
Karmody
Kadmod
pulses
Chevra
10) Identification of our cattle
Motive:- for identification of our cattle
Ways for our cattle identification:
1) Branding:- Branding is a type of cattle identification,
Serves to better Cattle Rustling,This also helps in returning rustled animals back home
Process of Branding Cattle:-
- Liquid Nitrogen or Denatured Nitrogen and Dry Ice are used to cool branding irons.
- Rather than burning the skin, freeze branding actually destroys the natural pigmentation of the animals hair,
- Making the hair of the cow on the branded area glow white.
Tatoo:- material- tatoo ink

like Branding,Tatoos can be used as a cattle identification.
Cattle needs to be secured properly before applying tatoo.
If any miscalculation the tatoo might appear blurry.
Ear tags:- These come in plastic or metal, can be custom numbered on one or both sides.
Permits at identifying animals from a distance,may eventually detach and get lost.
11) MURGRASS
Mur ghas is a food given to goats, cows, bulls. The grasses used in Mur ghasa are sorghum, elephant grass, and maize.
Method of making chicken:- First of all, the four should be roughly divided into two or three pieces.
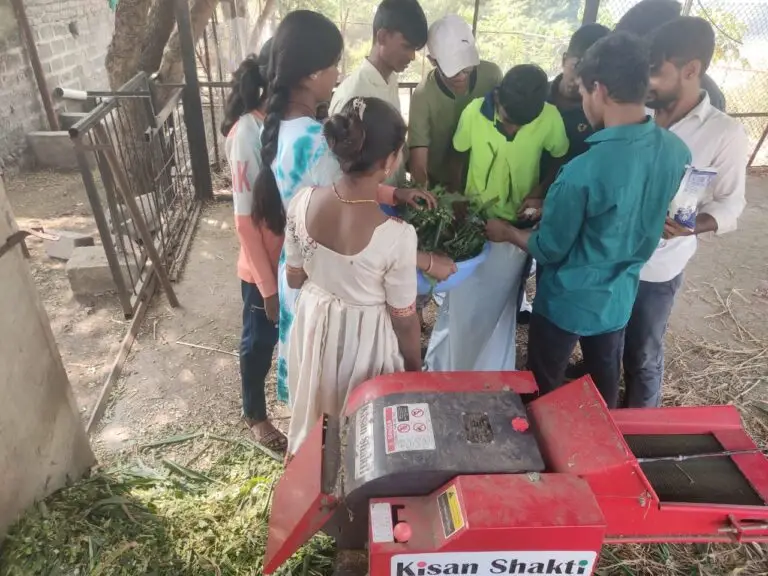

1)A first layer of fodder was applied in a bag, then a layer of salt and jaggery was applied on top of it, then again fodder was placed on top and again a layer of jaggery and salt was applied.
2)Now all these should be pressed down well with the help of foot which will expel all the air in it.
3) After this, the bag should be tied very tightly so that no air can get back into it. Because if air gets back in, all the feed will spoil.
12) FOGGER
Specification
(1)way Fogger

(2) way Fogger
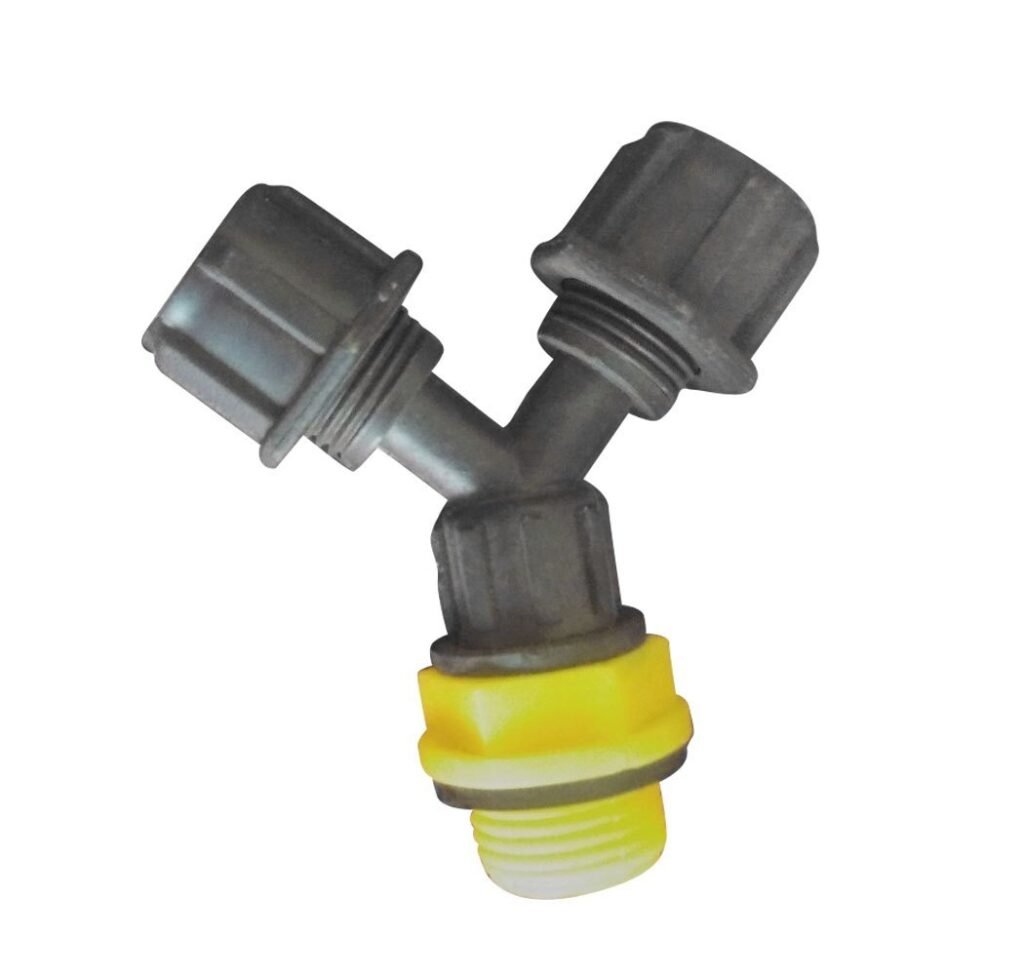

(4) way Fogger
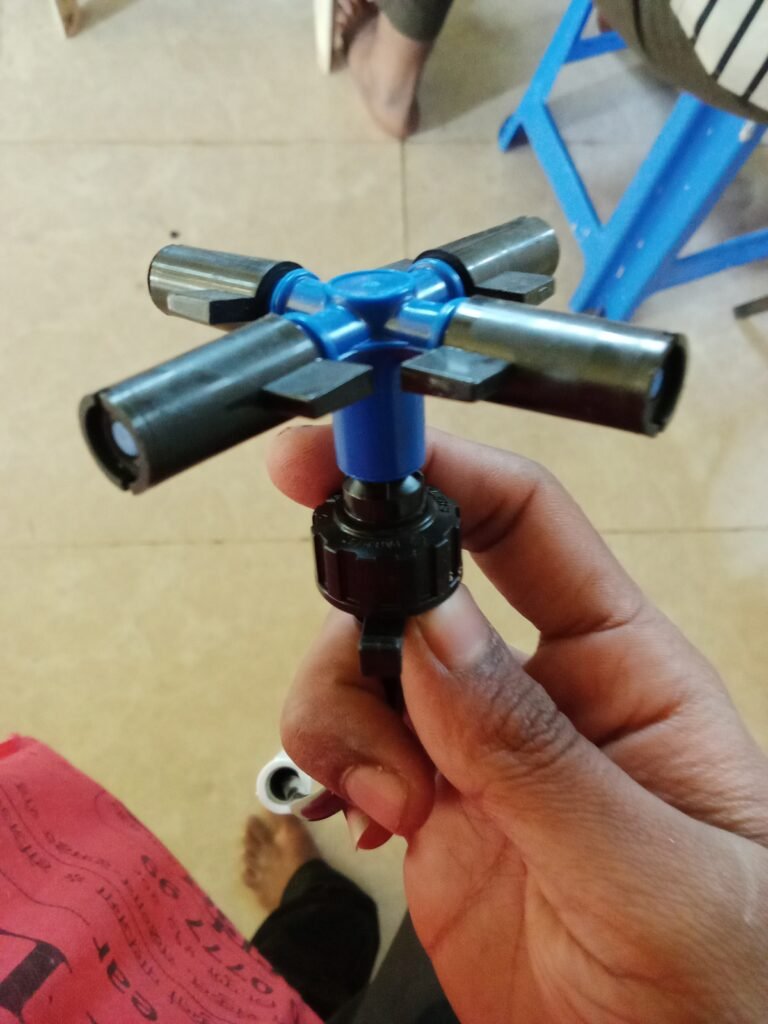

Hway Fogger are used in polyhouse
Flow rate = 28 LPH + I hazzel =7LPH Operating pree sune 2 kg/cm²/2har 28 PSI 1- 10 microns = 0.01mm 5-7℃
13) Milk extract method
Today I am going to tell you how to extract milk from animals.
In this we are going to see the methods of milking and their advantages and disadvantages.
Proper milking and proper maintenance is necessary while milking animals.
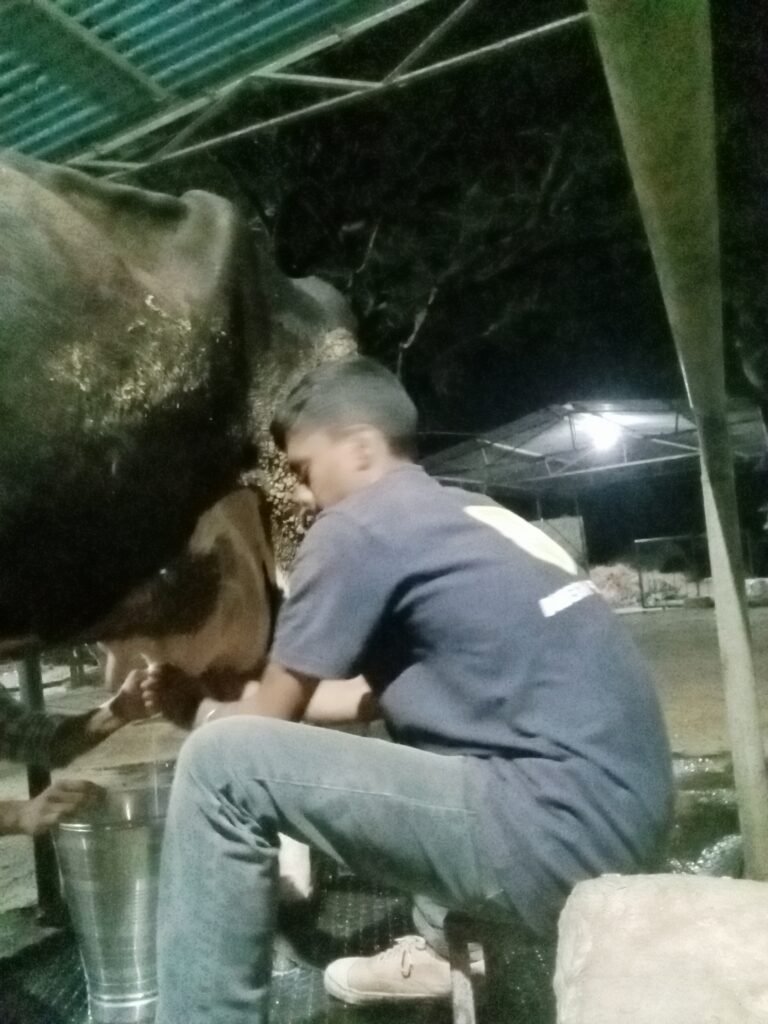

1) Milking by hand :-
1) Fist method :- This method is mainly used to extract milk from cow.
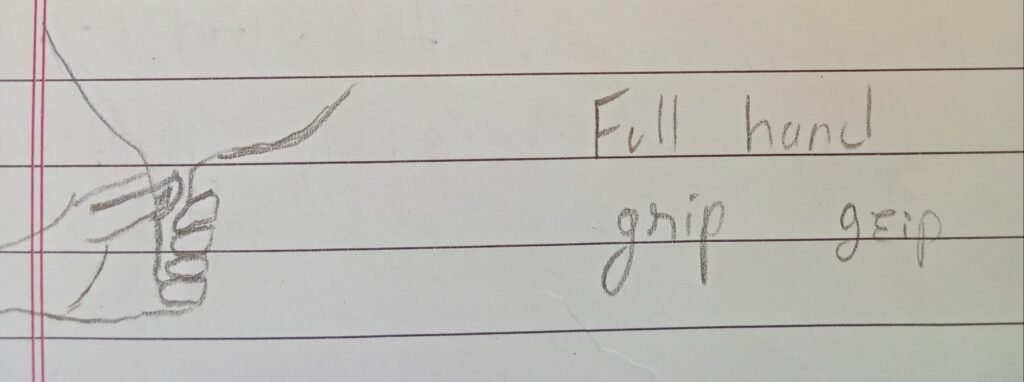
॥) Tweezing method: This method is mainly used to extract milk from animals like goat and sheep.
3) Thumb method This method is mainly used to extract milk from buffaloes.

14) Milk adulteration
Milk is adulterated to earn more profit from less milk. Water and various chemicals are used in this.
1) Water = To increase the quantity of milkWater is adulterated in milk. To check adulterated milk, a glass was taken and a drop of milk was left on it.
When that drop comes, he observes the line he has made. If the line is white then there is no adulteration in the Milk it is considered so, but if the white line is not melamine, then water has been mixed in it.
2) Melanin = When we add water to milk, the amount of protein in it decreases. It keeps on increasing. Melanin was added to it.
3) Formalin = Jab Formalin is added to increase the shelf life of milk.
4) Caustic Soda = Here this substance is used in large quantities for detergent, herbal. But the milk is white. To make foam.. add. Divya and here to add some foam to it.
5) Cone Flower = This cold ingredient is used to make the lassi a little thicker.Urea is added to increase the fat content in the milk.
15) Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis – The amazing process of making food by Plants photosynthesis is a unique and complex function of nature, which gives plants the ability to make their own food.
In this process, plants produce glucose (sugar) and oxygen with the help of sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere.
This process occurs only in green plants, algae, and some bacteria because they contain a pigment called chlorophyll,
Which absorbs the energy of the sun.The process of photosynthesis:Sunlight:Photosynthesis begins with sunlight.
The energy obtained from the sun is absorbed by the chlorophyll present in the leaves of the plant.
This light energy is converted into chemical energy, which is necessary for the further processWater:
The roots of the plant draw water from the soil and transport it to the leaves.
This water is a major component in photosynthesis and is used to make glucose. Carbon dioxide:Tiny pores in the leaves, called stomata, absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
This gas is also a part of the process of photosynthesis.Glucose:Plants produce glucose by combining sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. This glucose serves as food for plants and is used as energy.Oxygen:During this process, oxygen gas is also produced, which the plants release into the atmosphere.
This oxygen is life-giving for all living beings.
Chemical formula of photosynthesis:This means that 6 molecules of carbon dioxide and 6 molecules of water combine with the help of sunlight to form one molecule of glucose and 6 molecules of oxygen.Importance of photosynthesis:Photosynthesis is extremely important not only for plants but also for life on Earth.
This process not only provides food to plants but also helps in maintaining the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere. If this process had not happened, life on earth would not have been possible.
16) Poultry farming
Poultry means the business of producing chickens, fresh eggs and chicken meat.
This business is especially beneficial for farmers, as it can generate more income in less space.Source of income: Good profits are obtained from the sale of chickens and eggs.
Social needs: Eggs and chickens are important food for nutrition, which fulfill the dietary requirements of people.Fast growth: Chickens grow fast, so farmers get production in less time.
Low investment: Relatively less investment is required to start a poultry business.Major types of poultry farming:Fresh egg-laying chickens: In this type, eggs are obtained from chickens.
Meat producing chickens: This type of chickens are used for meat.Domestic chickens: These chickens are kept for special decoration.
Things to remember in poultry farming:Diet: It is very important to feed a balanced diet to chickens.
Health: Health of chickens needs to be monitored. Vaccination is mandatory for disease control.
Cleanliness: It is important to maintain cleanliness in poultry farms, so that diseases can be prevented from spreading.
17) Spring pump
Uses of spring pump
Spring pump is used in farm for fertilize the crop etc.
Types of spraying pump

1)Motor spring pump
3) Drone spring pump.
4) Tractor mount spring pump.
5) Mist pump sprayer
6) Hand sprayer
18) Tissue culture
Tissue Culture is the scientific method of growing or a a group part .
A plant by taking of a cell cell (tissue) from specific organ of it in a a test tube a plant.
In a Suitable artificial nutrient medium sterile and controlled environment laboratory.
tissue culture technique are advancing day by day It is also being used A Floriculture.
Tissue culture is a part of the modern science of te biotechnology to produce disease Free plant with the same genetic characteristics.
As the mother plant in a short period of time. First of all Dr. Morel a scientist in Fras used tissue culture in orchid .
19) Breed of chicken
Gririraj This breed of chicken are Famous. These chicken are different available colour. This breed is available for egg meat production .
A clay old of the Four and weighs 45 gm. The weight fully of this breed a half kg.
Vanraj – This egg by Hyderabad Poultry Project Bang Management at These Chickens are attractive and colourful in appearance
One day chink 40 50 gram The this chicken thighs bred toy go to female of lay 180 200 eggs per year.
Sahyadi – Satpudu breed is suitable for Ken kan environment and it has various colour Katak and immunity are high .
These hen lay 180 to 200 a year making the breed profitable for both egg and meat purposes.
Kalinga Brown – I This breed of Garpan chicken for highen productivity come on The Female of The breed 300 egg. per year an lay about 280 .
The average weight of egg of this hen is 54 grams. The Taste of the meat of this chicken is similar to that of native chicken.
Kadkonath: This breed are rane breed Ichickens ous chicken. These of indigenous ahe Famous For Theis medici Properties and tasty meat .
Also it is Known as black meat as the extern organ and the body are black in calour. This chickens have high immunity.
Foreign caste
White leg born: This breed of Italy Belong to to the village of leg horn m Fall into the light breed. It is white in colour graceful in appearance veny agile.
The average weight of and yery per weight se chicken is 30 grame per day
Hode Island – Red is native ta Hade Island prown Use as America they are ned and in coloun neared Fon dual meat and
the Female is up to 2 k, of chicken lay are lay brown in Color! The weight of This breed is. Se group.
Black leghan – This breed is famus for The chickens of this laying eggs blacked chi colour the breed are lagenge
Weight of the male weight and to 4 kg and the of the Female is 2 and a half to 3 kg. Egg weight is 50 to 60 grams.
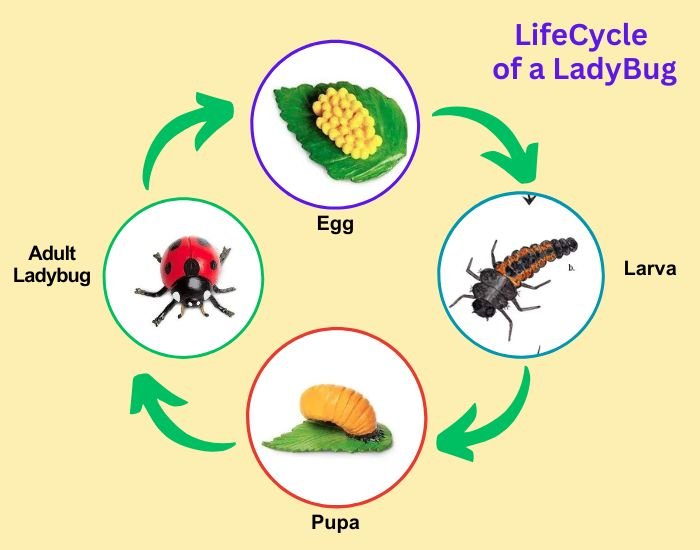
20) Insect life cycle
21) Polyhouse
iThis is fan pad polyhouse it works on evaporative cooling system which consist of cooling pad cellulose cooling pad exhaust fan .
also hydroponic system are there for crops grow . In there hydroponic system there are two main system are used deep water and NSC system are used in polyhouse.
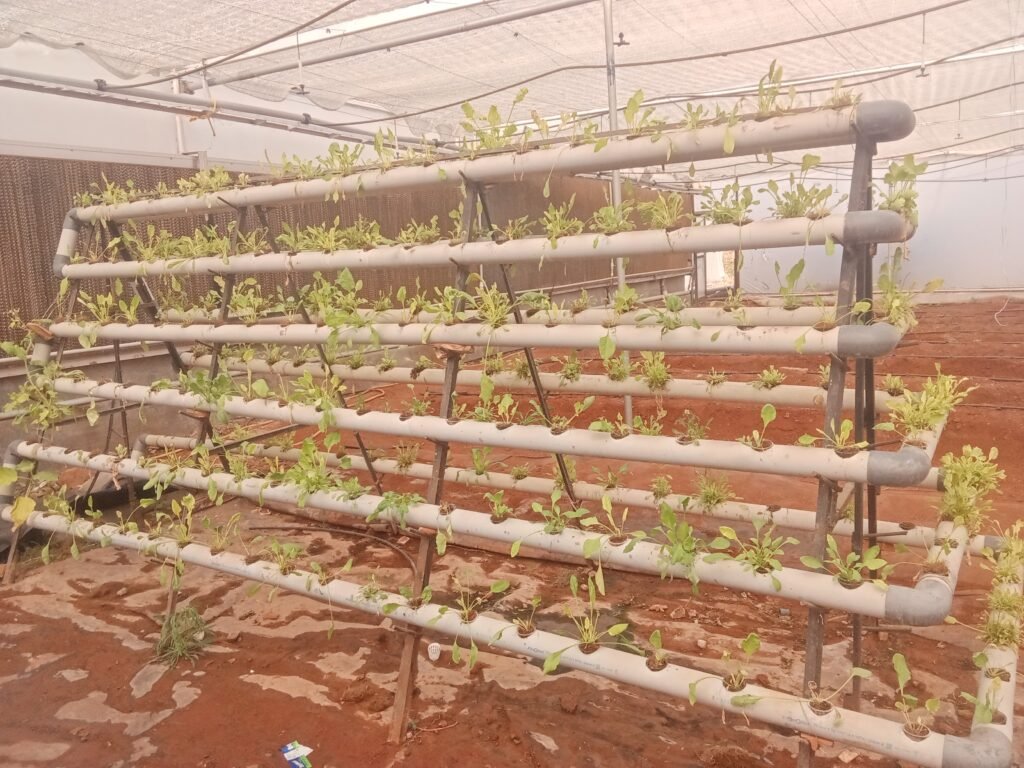

In NSC system plants grow with more nutrients everyday we maintain nutrients and pH level and EC everyday day they check of PH level in EC.
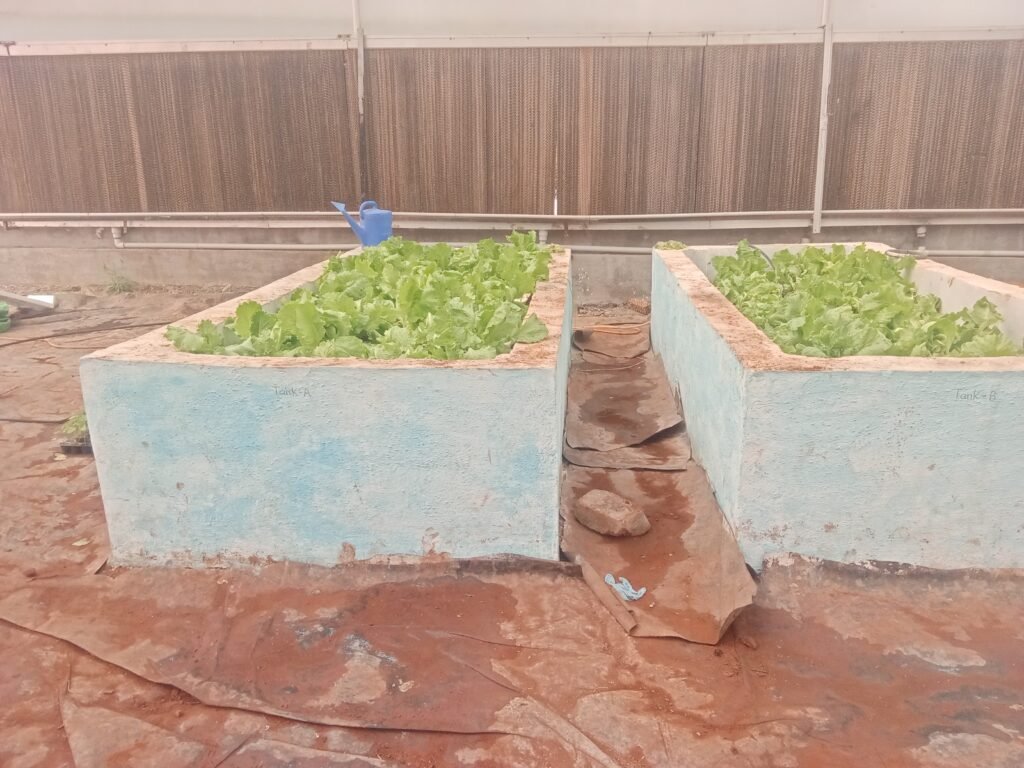

in deep water system plants get more nutrients but they have to gave more space also a bubbler used in deep water system for crops.
22) Cereal crops are grasses
Cereal crops are grasses that produce edible grains, such as wheat, rice, maize (corn), barley, oats, rye, and millet. These crops are a primary source of food, energy, and nutrients for humans and livestock.
Types of Cereal Crops
1. Wheat
One of the most widely grown cereal crops, used to make bread, pasta, and other baked goods.
2. Rice
A staple food for more than half of the world’s population, particularly in Asia.
3. Maize (Corn)
Used for food, animal feed, and biofuel production.
4. Barley
Used for animal feed, malt production, and human consumption.
5. Oats
Used for human consumption, animal feed, and other industrial applications.
6. Rye
Used for bread making, animal feed, and other industrial applications.
7. Millet
A small-grained cereal crop used for human consumption, animal feed, and other industrial
23) Weed control
Weed control is a type of pest control, which attempts to stop or reduce growth of weeds, especially noxious weeds,
With the aim of reducing their competition with desired flora and fauna including domesticated plants and livestock, and in natural settings preventing non native species competing with native species.
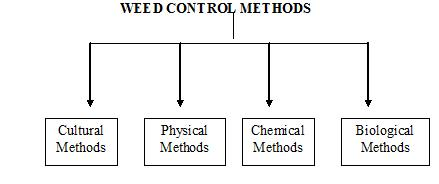
It’s considered to be the least harmful method to the environment, and it can be effective in controlling weeds in non-cropped areas.
Mechanical or physical methods of weed control are being employed ever since man began to grow crops.
The mechanical methods include tillage, hoeing, hand weeding, digging cheeling, sickling, mowing, burning, flooding, mulching etc.
Tillage removes weeds from the soil resulting in their death.
24) Animal feed like Dry Mentor
Dry Mentor is a type of dry animal feed, typically in the form of pellets or granules.
It’s designed to provide essential nutrients for livestock, poultry, and other animals.
The composition of Dry Mentor may vary depending on the manufacturer and specific formulation.
1. Grains (corn, wheat, barley)
2. Protein sources (soybean meal, fish meal)
3. Fiber sources (alfalfa meal, oat hulls)
4. Vitamins and minerals
5. Additives (antioxidants, preservatives)
Regularly check animals for signs of nutritional deficiencies or health issues.
Please consult with a veterinarian or animal nutritionist for specific guidance on using . Hydroponic system
25) Identification of food
The Ultimate Guide to Identifying Food:Tips and Tricks Vegetables.
vegetable.
For example, carrots are usually orange and cylindrical, while broccoli is green and tree-like.
Meat and poultry Look for characteristic cuts, colors, and textures. For example, chicken breasts are usually boneless and white, while beef steaks are often red and have visible marbling.
Culinary Clues Sometimes, the way a food is prepared or presented can give away its identity Cooking methods Look for characteristic cooking methods, such as grilling, roasting, or frying.
Sauces and seasonings Observe the types of sauces or seasonings used, as these can be clues to the food’s identity.
Cultural associations Consider the cultural or regional associations of a particular .
26) Figuring out a frost irrigation system
Components of a Frost Irrigation System
1. Water Source A reliable water source, such as a well or pond, is necessary to supply water to the system.
2. Pumps Pumps are used to pressurize the water and distribute it throughout the system.
3. Pipes and Fittings
A network of pipes and fittings is used to distribute water to the crops.
4. Sprinklers or Micro-Irrigation Sprinklers or micro-irrigation systems are used to apply water to the crops.
5. Control SystemA control system, such as a timer or sensor, is used to automate the system and ensure that water is applied only during frost events.
A Frost Irrigation System Works
1. Frost Detection The control system detects frost conditions, either through temperature sensors or other means.
2. Water
Application When frost is detected, the control system activates the pumps and water is applied to the crops through the sprinklers or micro-irrigation system.
3. Ice Formation
As the water is applied, it forms a layer of ice on the surface of the crops.
4. Heat
Release As the water freezes, it releases heat, which helps to protect the crops from damage.
1. Crop Protection
A frost irrigation system can help protect crops from frost damage, reducing crop loss and improving yields.
2. Water Conservation
By applying water only during frost events, a frost irrigation system can help conserve water.
3. Automated Operation
A frost irrigation system can be automated, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimize the risk of human error.
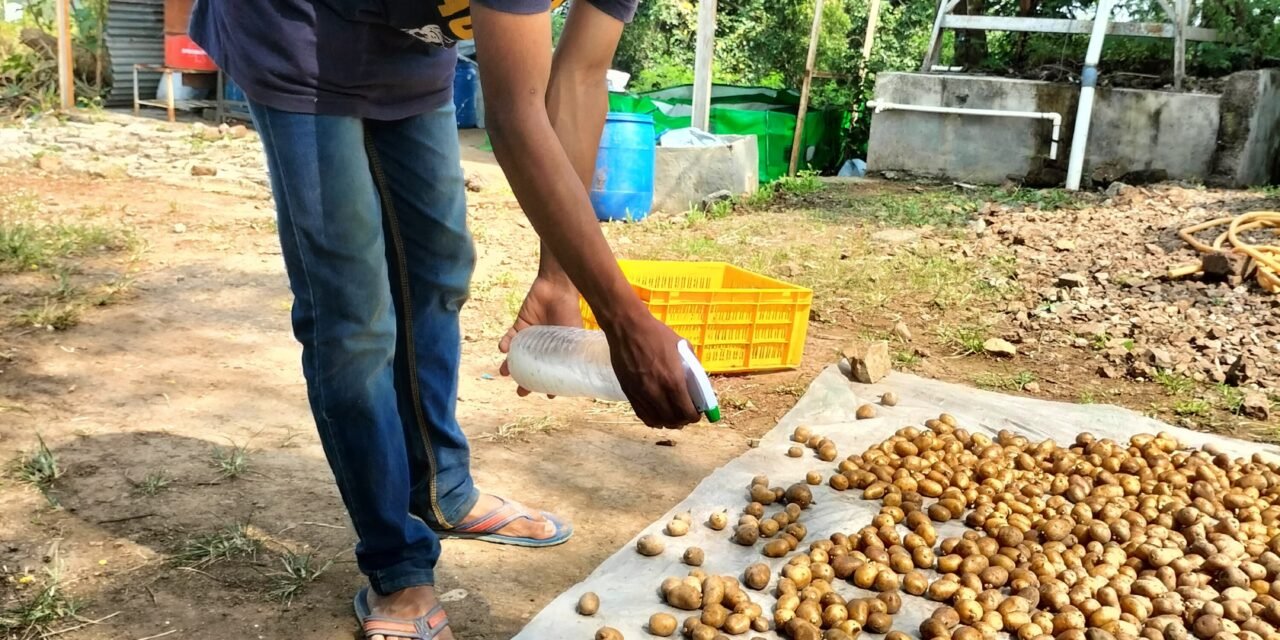
27) Preparing the spray solution
General Instructions
1.Read the label
Before preparing the spray solution, read the label on the pesticide or fertilizer container to ensure you understand the instructions and any safety precautions.
2. Wear protective gear
Wear protective clothing, including gloves, safety glasses, and a mask, to prevent exposure to the pesticide or fertilizer.
3. Use clean equipment
Use clean and sanitized equipment to prevent contamination of the spray solution.
Preparation
Measure the pesticide or fertilizer
Measure the recommended amount of pesticide or fertilizer using a calibrated measuring cup or scale.
2. Measure the water
Measure the recommended amount of water using a calibrated measuring cup or scale.
3. Mix the solution
Mix the pesticide or fertilizer with the water in a well-ventilated area. Start by adding the pesticide or fertilizer to the water, and then stir the solution thoroughly.
4. Add any required adjuvants
Add any required adjuvants, such as surfactants or wetting agents, to the solution and stir thoroughly.
5. Check the pH
Check the pH of the solution using pH test strips or a pH meter. Adjust the pH if necessary.
6. Filter the solution
Filter the solution through a cheesecloth or a fine-mesh filter to remove any sediment or debris.
Safety Precautions
1. Avoid skin contact
Avoid skin contact with the pesticide or fertilizer, as it can cause irritation or other health problems.
2. Avoid inhalation
Avoid inhaling the spray solution, as it can cause respiratory problems.
3. Wash hands thoroughly Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling the pesticide or fertilizer.
4. Dispose of waste properly
Dispose of any waste, including empty containers and leftover solution, according to the manufacturer’s instructions .
28) Measuring Dry Matter
Measuring Dry Matter: A Simple Guide have you ever wondered how to measure the water content of a substance?
Whether you’re a farmer, food manufacturer, or soil scientist, understanding dry matter content is crucial.
What is Dry Matter?
Dry matter refers to the solid parts of a substance, excluding water. It’s an essential parameter in various fields, including agriculture, food processing, and soil science.
Methods for Measuring Dry MatterThere are several ways to measure dry matter content:
1. Oven Drying: This involves heating the sample in an oven to evaporate the water, leaving behind the dry matter.
2. Freeze Drying: This method involves freezing the sample and then reducing the surrounding pressure to allow the frozen water to sublimate (change directly from a solid to a gas) without going through the liquid phase.
3. Microwave Drying: This method uses microwave energy to heat the sample and evaporate the water.
4. Desiccation: This involves placing the sample in a desiccator, a sealed container with a desiccant (a substance that absorbs moisture), to remove the water.
Calculating Dry Matter ContentTo calculate dry matter content, you can use the following formula:Dry Matter (%) = (Dry Weight / Wet Weight) x 100Where:- Dry Weight is the weight of the sample after drying
Wet Weight is the weight of the sample before drying
Why is Dry Matter Content Important?Understanding dry matter content is crucial in various fields:
1. Agriculture: Dry matter content helps determine crop quality and yield.
2. Food Processing: Dry matter content helps optimize food processing conditions and ensure product quality.
3. Soil Science: Dry matter content helps determine soil moisture content .
29) Hydroponic system
hydroponic system are there for crops grow . In there hydroponic system.
There are two main system are used deep water and NSC system are used in polyhouse.
In NSC system plants grow with more nutrients everyday we maintain nutrients .
pH level and EC everyday day they check of PH level in EC.
in deep water system plants get more nutrients but they have to gave more space.
Also a bubbler used in deep water system for crops.
we are using chemicals to control EC and pH level after controlling EC pH level we get a result of growth of crop
everyday we take sample of water and checking easy and pH level in the lab.
we get a result in 2 days after getting result we can use a chemical or nutrients for crops.
30) Creating a nursery
first step of creating nursery
when using grafting technique.we can make nursery
Step 1: Plan and PrepareBefore you start setting up the nursery, take some time to plan and prepare.
Here are a few things to consider: Choose a quiet and well-ventilated area with plenty of natural light.Set a budget for the nursery setup and equipment.
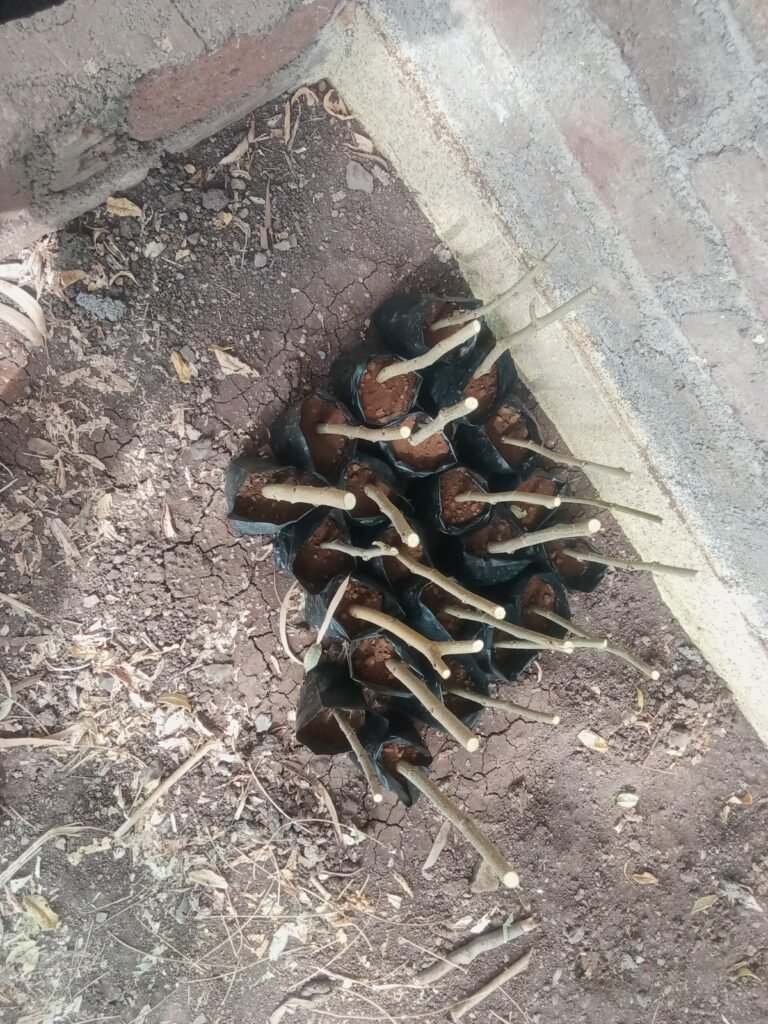

Think about the overall theme and style of the nursery.Measure the room to ensure that the furniture fits comfortably.
Step 2: Decor and Accessories Now it’s time to add some personality and style to the nursery:
Hang some beautiful wall art or decals to create a visually interesting space.Add some comfortable rugs and mats to the floor.
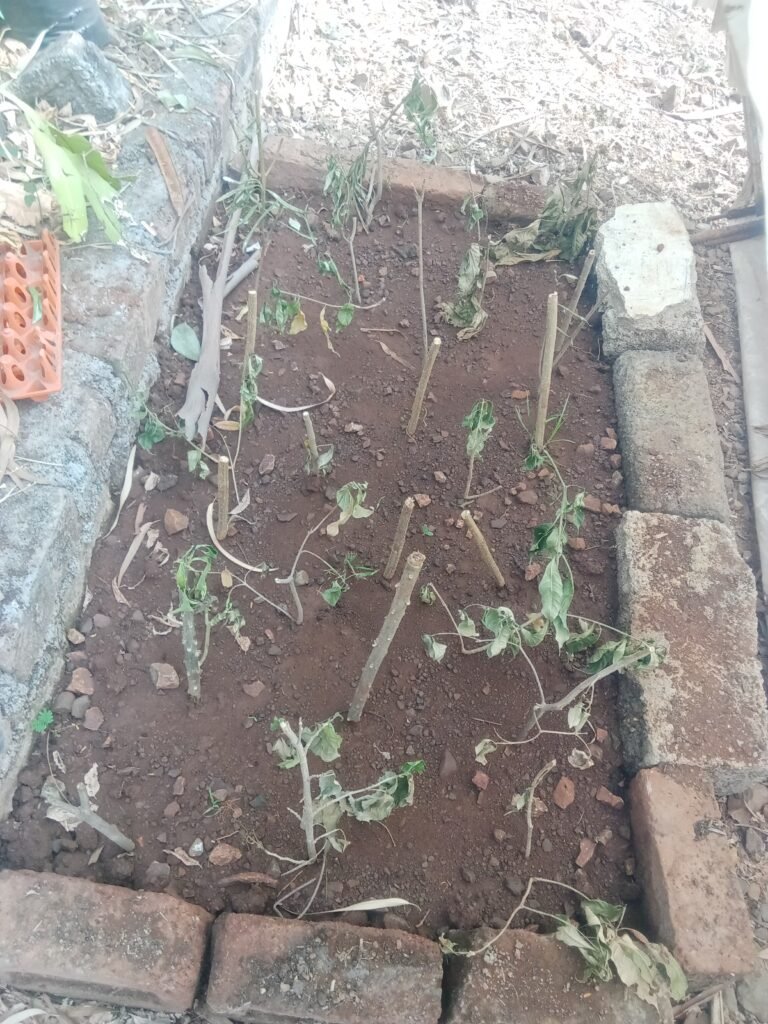

Install some curtains or blinds to control the light and create a cozy atmosphere. Bring in some plants or greenery to add a touch of nature .



